Module API
py_trees_ros
ROS extensions, behaviours and utilities for py_trees.
py_trees_ros.action_clients
- class py_trees_ros.action_clients.FromBlackboard(name, action_type, action_name, key, generate_feedback_message=None, wait_for_server_timeout_sec=-3.0)[source]
Bases:
BehaviourAn action client interface that draws goals from the blackboard. The lifecycle of this behaviour works as follows:
initialise(): check blackboard for a goal and sendupdate(): if a goal was sent, monitor progressterminate(): if interrupted while running, send a cancel request
As a consequence, the status of this behaviour can be interpreted as follows:
FAILURE: no goal was found to send, it was rejected or it failed while executingRUNNING: a goal was sent and is still executing on the serverSUCCESS: sent goal has completed with success
To block on the arrival of a goal on the blackboard, use with the
py_trees.behaviours.WaitForBlackboardVariablebehaviour. e.g.sequence = py_trees.composites.Sequence(name="Sequence", memory=True) wait_for_goal = py_trees.behaviours.WaitForBlackboardVariable( name="WaitForGoal", variable_name="/my_goal" ) action_client = py_trees_ros.aciton_clients.FromBlackboard( action_type=py_trees_actions.Dock, action_name="dock", name="ActionClient" ) sequence.add_children([wait_for_goal, action_client])
To customise a more interesting feedback message, pass in a method to the constructor, for example:
action_client = py_trees_ros.action_clients.FromBlackboard( action_type=py_trees_actions.Dock, action_name="dock", name="ActionClient", generate_message=lambda msg: "{:.2f}%%".format(msg.feedback.percentage_completed) )
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the behaviour
action_type (Any) – spec type for the action (e.g. move_base_msgs.action.MoveBase)
action_name (str) – where you can find the action topics & services (e.g. “bob/move_base”)
key (str) – name of the key on the blackboard
generate_feedback_message (Callable[[Any], str]) – formatter for feedback messages, takes action_type.Feedback messages and returns strings (default: None)
wait_for_server_timeout_sec (float) – use negative values for a blocking but periodic check (default: -3.0)
Note
The default setting for timeouts (a negative value) will suit most use cases. With this setting the behaviour will periodically check and issue a warning if the server can’t be found. Actually aborting the setup can usually be left up to the behaviour tree manager.
- cancel_response_callback(future)[source]
Immediate callback for the result of a cancel request. This will set the behaviour’s feedback message accordingly.
- Parameters
future (rclpy.task.Future) – incoming cancellation result delivered from the action server
- feedback_callback(msg)[source]
Default generator for feedback messages from the action server. This will update the behaviour’s feedback message with a stringified version of the incoming feedback message.
- Parameters
msg (Any) – incoming feedback message (e.g. move_base_msgs.action.MoveBaseFeedback)
- get_result_callback(future)[source]
Immediate callback for the result, saves data into local variables so that the update method can react accordingly.
- Parameters
future (rclpy.task.Future) – incoming goal result delivered from the action server
- goal_response_callback(future)[source]
Handle goal response, proceed to listen for the result if accepted.
- Parameters
future (rclpy.task.Future) – incoming goal request result delivered from the action server
- send_cancel_request()[source]
Send a cancel request to the server. This is triggered when the behaviour’s status switches from
RUNNINGtoINVALID(typically a result of a priority interrupt).
- send_goal_request(goal)[source]
Send the goal, get a future back and start lining up the chain of callbacks that will lead to a result.
- Parameters
goal (Any) –
- setup(**kwargs)[source]
Setup the action client services and subscribers.
- Parameters
**kwargs (
dict) – distribute arguments to this behaviour and in turn, all of it’s children- Raises
KeyError – if a ros2 node isn’t passed under the key ‘node’ in kwargs
TimedOutError – if the action server could not be found
- terminate(new_status)[source]
If running and the current goal has not already succeeded, cancel it.
- Parameters
new_status (Status) – the behaviour is transitioning to this new status
- class py_trees_ros.action_clients.FromConstant(name, action_type, action_name, action_goal, generate_feedback_message=None, wait_for_server_timeout_sec=-3.0)[source]
Bases:
FromBlackboardConvenience version of the action client that only ever sends the same goal.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the behaviour
action_type (Any) – spec type for the action (e.g. move_base_msgs.action.MoveBase)
action_name (str) – where you can find the action topics & services (e.g. “bob/move_base”)
action_goal (Any) – the goal to send
generate_feedback_message (Callable[[Any], str]) – formatter for feedback messages, takes action_type.Feedback messages and returns strings (default: None)
wait_for_server_timeout_sec (float) – use negative values for a blocking but periodic check (default: -3.0)
Note
The default setting for timeouts (a negative value) will suit most use cases. With this setting the behaviour will periodically check and issue a warning if the server can’t be found. Actually aborting the setup can usually be left up to the behaviour tree manager.
py_trees_ros.battery
Getting the most out of your battery.
- class py_trees_ros.battery.ToBlackboard(name, topic_name, qos_profile, threshold=30.0)[source]
Bases:
ToBlackboardSubscribes to the battery message and writes battery data to the blackboard. Also adds a warning flag to the blackboard if the battery is low - note that it does some buffering against ping-pong problems so the warning doesn’t trigger on/off rapidly when close to the threshold.
When ticking, updates with
RUNNINGif it got no data,SUCCESSotherwise.- Blackboard Variables:
battery (
sensor_msgs.msg.BatteryState)[w]: the raw battery messagebattery_low_warning (
bool)[w]: False if battery is ok, True if critically low
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the behaviour
topic_name (str) – name of the battery state topic
qos_profile (rclpy.qos.QoSProfile) – qos profile for the subscriber
threshold (float) – percentage level threshold for flagging as low (0-100)
py_trees_ros.blackboard
This module provides the py_trees_ros.blackboard.Exchange class,
a ROS wrapper around a
Blackboard that permits
introspection of either the entire board or a window onto a smaller part
of the board over a ROS API via the py-trees-blackboard-watcher
command line utility.
- class py_trees_ros.blackboard.BlackboardView(node, topic_name, variable_names, filter_on_visited_path, with_activity_stream)[source]
Bases:
objectUtility class that enables tracking and publishing of relevant parts of the blackboard for a user. This is used by the
Exchangeoperator.- Parameters
node (rclpy.node.Node) – an rclpy node for communications handling
topic_name (str) – name of the topic for the publisher
filter_on_visited_path (bool) – constrain dynamically to the visited region of the blackboard
with_activity_stream (bool) –
- is_changed(visited_clients)[source]
Dynamically adjusts the tracking parameters for the sub-blackboard against the clients that were visited (if desired) and proceeds to determine if there was a change since the last check.
Warning
Since this caches the current blackboard, it can’t be used multiple times in succession.
- class py_trees_ros.blackboard.BlackboardWatcher(namespace_hint=None)[source]
Bases:
objectThe blackboard watcher sits on the other side of the exchange and is a useful mechanism from which to pull all or part of the blackboard contents. This is useful for live introspection, or logging of the blackboard contents.
- Parameters
namespace_hint (str) – (optionally) used to locate the blackboard if there exists more than one
See also
- create_service_client(key)[source]
Convenience api for opening a service client and waiting for the service to appear.
- Parameters
key (str) – one of ‘open’, ‘close’.
- Raises
NotReadyError – if setup() wasn’t called to identify the relevant services to connect to.
TimedOutError – if it times out waiting for the server
- echo_blackboard_contents(msg)[source]
Very simple formatter of incoming messages.
- Parameters
msg (
std_msgs.String) – incoming blackboard message as a string.
- setup(timeout_sec)[source]
Creates the node and checks that all of the server-side services are available for calling on to open a connection.
- Parameters
timeout_sec (float) – time (s) to wait (use common.Duration.INFINITE to block indefinitely)
- Raises
NotFoundError – if no services were found
MultipleFoundError – if multiple services were found
- class py_trees_ros.blackboard.Exchange[source]
Bases:
objectEstablishes ros communications around a
Blackboardthat enable users to introspect or watch relevant parts of the blackboard.- ROS Publishers:
~/_watcher_<N> (
std_msgs.msg.String)streams the (sub)blackboard over a blackboard watcher connection
- ROS Services:
~/get_variables (
py_trees_msgs.srv.GetBlackboardVariables)list all the blackboard variable names (not values)
~/open (
py_trees_msgs.srv.OpenBlackboardStream)request a publisher to stream a part of the blackboard contents
~/close (
py_trees_msgs.srv.CloseBlackboardStream)close a previously opened watcher
Watching could be more simply enabled by just providing a get style service on a particular variable(s), however that would introduce an asynchronous interrupt on the library’s usage and subsequently, locking. Instead, a watcher service requests for a stream, i.e. a publisher to be created for private use that streams only a subsection of the blackboard to the user. Additional services are provided for closing the stream and listing the variables on the blackboard.
See also
py_trees_ros.trees.BehaviourTree(in which it is used) and py-trees-blackboard-watcher (working with the watchers).- post_tick_handler(visited_client_ids=None)[source]
Update blackboard watcher views, publish changes and clear the activity stream. Publishing is lazy, depending on blackboard watcher connections.
Typically you would call this from a tree custodian (e.g.
py_trees_ros.trees.BehaviourTree) after each and every tick.
- setup(node)[source]
This is where the ros initialisation of publishers and services happens. It is kept outside of the constructor for the same reasons that the familiar py_trees
setup()method has - to enable construction of behaviours and trees offline (away from their execution environment) so that dot graphs and other visualisations of the tree can be created.- Parameters
node (
Node) – node to hook ros communications on
Examples
It is expected that users will use this in their own customised tree custodian:
class MyTreeManager(py_trees.trees.BehaviourTree): def __init__(self): pass def setup(self, timeout): super(MyTreeManager, self).setup(timeout) self.exchange = py_trees_ros.blackboard.Exchange() self.exchange.setup(timeout)
See also
This class is used as illustrated above in
BehaviourTree.
- class py_trees_ros.blackboard.SubBlackboard(node)[source]
Bases:
objectDynamically track the entire blackboard or part thereof and flag when there have been changes. This is a nice to have that only works if the blackboard contains fundamental variables (i.e. objects that can be pickled).
- Parameters
node (rclpy.node.Node) – the node handle for ros logging of warnings if needed
py_trees_ros.conversions
Converter methods for transferring information back and forth between py_trees objects and ros messages.
- py_trees_ros.conversions.activity_stream_to_msgs()[source]
Convert the blackboard activity stream to a message.
- Returns
A list of activity item messages.
- Return type
List[<Mock name=’mock.msg.ActivityItem’ id=’140605245237824’>]
- py_trees_ros.conversions.additional_detail_to_str(behaviour)[source]
Provide, e.g. policy information about the behaviour (i.e. black magic details under the hood). Useed for debugging, so only strings needed.
Todo
Unlock unicode support across the wire, currently only ascii arrives ungarbled.
- py_trees_ros.conversions.behaviour_to_msg(behaviour)[source]
Convert a behaviour to a message.
- Parameters
behaviour (Behaviour) – behaviour to convert
- Returns
a ros message representation of a behaviour
- Return type
<Mock name=’mock.msg.Behaviour’ id=’140605245237488’>
- py_trees_ros.conversions.behaviour_type_to_msg_constant(behaviour)[source]
Convert a behaviour class type to a message constant.
- Parameters
behaviour (Behaviour) – investigate the type of this behaviour
- Returns
from the type constants in
py_trees_ros_interfaces.msg.Behaviour- Return type
uint8
- py_trees_ros.conversions.blackbox_enum_to_msg_constant(blackbox_level)[source]
Convert a blackbox level enum to a message constant.
- Parameters
blackbox_level (BlackBoxLevel) – blackbox level of a behaviour
- Returns
from the type constants in
py_trees_ros_interfaces.msg.Behaviour- Return type
uint8
- py_trees_ros.conversions.msg_constant_to_behaviour_type(value)[source]
Convert one of the behaviour type constants in a
py_trees_ros_interfaces.msg.Behaviourmessage to a type.- Parameters
value (int) – see the message definition for details
- Returns
a behaviour class type (e.g.
py_trees.composites.Sequence)- Raises
TypeError – if the message type is unrecognised
- Return type
- py_trees_ros.conversions.msg_constant_to_blackbox_level_enum(value)[source]
Convert one of the blackbox level constants in a
Behaviourmessage to a py_trees status enum.
- py_trees_ros.conversions.msg_constant_to_status_enum(value)[source]
Convert one of the status constants in a
py_trees_ros_interfaces.msg.Behaviourmessage to a py_trees status enum.
- py_trees_ros.conversions.msg_to_behaviour(msg)[source]
Convert behaviour message to a py_trees behaviour. This doesn’t completely recreate the original behaviour (doesn’t have any of the custom state), but allows the user to compose a tree that can be utilised for debugging or visualisation applications.
- Parameters
msg (<Mock name='mock.msg.Behaviour' id='140605245237488'>) – a ros message representation of a behaviour
- Returns
converted, skeleton of the original behaviour
- Return type
- py_trees_ros.conversions.msg_to_uuid4(msg)[source]
Convert a uuid4 python object to a ros unique identifier, UUID type.
- Parameters
msg (<Mock name='mock.msg.UUID' id='140605245237776'>) – the ros message type
- Returns
the behaviour’s uuid, python style
- Return type
- py_trees_ros.conversions.rclpy_duration_to_float(duration)[source]
Convert a ros2 duration (seconds/nanoseconds) to a float.
- Parameters
time – time to convert
duration (rclpy.time.Duration) –
- Returns
time (seconds) as a float
- Return type
- py_trees_ros.conversions.rclpy_time_to_float(time)[source]
Convert a ros2 time (seconds/nanoseconds) to a float.
- Parameters
time (rclpy.time.Time) – time to convert
- Returns
time (seconds) as a float
- Return type
- py_trees_ros.conversions.status_enum_to_msg_constant(status)[source]
Convert a status to a message constant.
- Parameters
status (Status) – status enum of a behaviour
- Returns
from the status constants in
py_trees_ros_interfaces.msg.Behaviour- Return type
uint8
- py_trees_ros.conversions.uuid4_to_msg(uuid4=UUID('4274e85a-7a5f-46d5-98ac-58cea39e68d5'))[source]
Convert a uuid4 python object to a ros unique identifier, UUID type.
- Parameters
uuid4 (UUID) – unique identifier to convert, defaults to auto-generated uuid4
- Returns
the ros message type
- Return type
<Mock name=’mock.msg.UUID’ id=’140605245237776’>
py_trees_ros.exceptions
Custom exception types for py_trees_ros.
- exception py_trees_ros.exceptions.MultipleFoundError[source]
Bases:
ExceptionMiddleware connection found when but one was expected.
- exception py_trees_ros.exceptions.NotFoundError[source]
Bases:
ExceptionMiddleware connection not found.
- exception py_trees_ros.exceptions.NotReadyError[source]
Bases:
ExceptionTypically used when methods have been called that expect, but have not pre-engaged in the ROS2 specific setup typical of py_trees_ros classes and behaviours.
py_trees_ros.publishers
Convenience behaviours for publishing ROS messages.
- class py_trees_ros.publishers.FromBlackboard(name, topic_name, topic_type, qos_profile, blackboard_variable)[source]
Bases:
BehaviourThis behaviour looks up the blackboard for content to publish … and publishes it.
This is a non-blocking behaviour - if there is no data yet on the blackboard it will tick with
FAILURE, otherwiseSUCCESS.To convert it to a blocking behaviour, simply use with the
py_trees.behaviours.WaitForBlackboardVariable. e.g.sequence = py_trees.composites.Sequence(name="Sequence", memory=True) wait_for_data = py_trees.behaviours.WaitForBlackboardVariable( name="WaitForData", variable_name="/my_message" ) publisher = py_trees_ros.publishers.FromBlackboard( topic_name="/foo", topic_type=std_msgs.msg.Empty qos_profile=my_qos_profile, blackboard_variable="/my_message" ) sequence.add_children([wait_for_data, publisher])
The various set/unset blackboard variable behaviours can also be useful for setting and unsetting the message to be published (typically elsewhere in the tree).
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the behaviour
topic_name (str) – name of the topic to connect to
topic_type (Any) – class of the message type (e.g.
std_msgs.msg.String)qos_profile (rclpy.qos.QoSProfile) – qos profile for the subscriber
blackboard_variable (str) – name of the variable on the blackboard (can be nested)
py_trees_ros.subscribers
ROS subscribers are asynchronous communication handles whilst py_trees are by their nature synchronous. They tick, pause, then tick again and provide an assumption that only one behaviour or function is running at any single moment. Firing off a subscriber callback in the middle of that synchronicity to write to a blackboard would break this assumption.
To get around that, subscriber behaviours run the ros callbacks in a background thread and constrain locking and a local cache inside the behaviour. Only in the update function is a cached variable unlocked and then permitted to be used or written to the blackboard.
- class py_trees_ros.subscribers.CheckData(name, topic_name, topic_type, qos_profile, variable_name, expected_value, comparison_operator=<built-in function eq>, fail_if_no_data=False, fail_if_bad_comparison=False, clearing_policy=ClearingPolicy.ON_INITIALISE)[source]
Bases:
HandlerCheck a subscriber to see if it has received data.
It optionally checks whether that data, or part of it has a specific value.
Usage Patterns
Sequence Guard:
RUNNINGuntil there is a successful comparisonfail_if_no_data=False
fail_if_bad_comparison=False
Selector Priority Chooser:
FAILUREuntil there is a successful comparisonfail_if_no_data=True
fail_if_bad_comparison=True
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the behaviour
topic_name (str) – name of the topic to connect to
topic_type (Any) – class of the message type (e.g.
std_msgs.msg.String)qos_profile (rclpy.qos.QoSProfile) – qos profile for the subscriber
variable_name (str) – name of the variable to check
expected_value (Any) – expected value of the variable
comparison_operator – one from the python operator module
fail_if_no_data –
FAILUREinstead ofRUNNINGif there is no data yetfail_if_bad_comparison –
FAILUREinstead ofRUNNINGif comparison failedclearing_policy – when to clear the data
Tip
Prefer
ToBlackboardand the various blackboard checking behaviours instead. It will provide you with better introspection capability and less complex behaviour construction to manage.
- class py_trees_ros.subscribers.EventToBlackboard(name, topic_name, qos_profile, variable_name)[source]
Bases:
HandlerListen for events (
std_msgs.msg.Empty) on a subscriber and writes the result to the blackboard.This will write True to the variable on the blackboard if a message was received since the last tick, False otherwise. The behaviour itself always returns
SUCCESS.Tip
Ideally you need this at the very highest part of the tree so that it gets triggered every time - once this happens, then the rest of the behaviour tree can utilise the variables.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the behaviour
topic_name (str) – name of the topic to connect to
qos_profile (rclpy.qos.QoSProfile) – qos profile for the subscriber
variable_name (str) – name to write the boolean result on the blackboard
- class py_trees_ros.subscribers.Handler(name, topic_name, topic_type, qos_profile, clearing_policy=ClearingPolicy.ON_INITIALISE)[source]
Bases:
BehaviourWarning
Do not use - it will always return
INVALID. Subclass it to create a functional behaviour.Not intended for direct use, as this just absorbs the mechanics of setting up a subscriber for inheritance by user-defined behaviour classes. There are several options for the mechanism of clearing the data so that a new result can be processed.
Always Look for New Data
This will clear any currently stored data upon entry into the behaviour (i.e. when
initialise()is called). This is useful for a behaviour in a sequence that is looking to start fresh as it is about to tick and be in aRUNNINGstate until new data arrives.Look for New Data only after SUCCESS
This will clear any currently stored data as soon as the behaviour returns
SUCCESS. This is useful for catching new triggers/events from things like buttons where you don’t want to miss things even though you may not actually be ticking.Use the Latest Data
Even if this data was received before entry into the behaviour. In this case
initialise()does not do anything with the currently stored data. Useful as a blocking behaviour to wait on some some topic having been initialised with some data (e.g. CameraInfo).- Parameters
name (str) – name of the behaviour
topic_name (str) – name of the topic to connect to
topic_type (Any) – class of the message type (e.g.
std_msgs.msg.String)qos_profile (rclpy.qos.QoSProfile) – qos profile for the subscriber
clearing_policy (ClearingPolicy) – when to clear the data
- initialise()[source]
If the clearing policy is set to
ON_INITIALISEit will clear the internally saved message, otherwise it does nothing.
- class py_trees_ros.subscribers.ToBlackboard(name, topic_name, topic_type, qos_profile, blackboard_variables={}, initialise_variables={}, clearing_policy=ClearingPolicy.ON_INITIALISE)[source]
Bases:
HandlerSaves the latest message to the blackboard and immediately returns success. If no data has yet been received, this behaviour blocks (i.e. returns RUNNING).
Typically this will save the entire message, however sub fields can be designated, in which case they will write to the specified keys.
- Parameters
topic_name (str) – name of the topic to connect to
topic_type (Any) – class of the message type (e.g.
std_msgs.msg.String)qos_profile (rclpy.qos.QoSProfile) – qos profile for the subscriber
blackboard_variables (Dict[str, Any]) – blackboard variable string or dict {names (keys) - message subfields (values)}, use a value of None to indicate the entire message
initialise_variables (Dict[str, Any]) – initialise the blackboard variables to some defaults
name (str) – name of the behaviour
clearing_policy – when to clear the data
Examples
To capture an entire message:
chatter_to_blackboard = ToBlackboard(topic_name="chatter", topic_type=std_msgs.msg.String, blackboard_variables = {'chatter': None} )
or to get rid of the annoying sub-data field in std_msgs/String:
chatter_to_blackboard = ToBlackboard(topic_name="chatter", topic_type=std_msgs.msg.String, blackboard_variables = {'chatter': 'data'} )
combinations of multiple entities inside the message can also be saved:
blackboard_variables={"pose_with_covariance_stamped": None, "pose": "pose.pose"}
- class py_trees_ros.subscribers.WaitForData(name, topic_name, topic_type, qos_profile, clearing_policy=ClearingPolicy.ON_INITIALISE)[source]
Bases:
HandlerWaits for a subscriber’s callback to be triggered. This doesn’t care about the actual data, just whether it arrived or not, so is useful for catching triggers (std_msgs/Empty messages) or blocking (in the behaviour sense) until some data has arrived (e.g. camera configuration). There are two use cases:
Usage Patterns
Got Something, Sometime
clearing_policy ==
NEVER
Don’t care when data arrived, just that it arrived. This could be for something like a map topic, or a configuration that you need to block. Once it returns
SUCCESS, it will always returnSUCCESS.Wating for the Next Thing, Starting From Now
clearing_policy ==
ON_INTIALISE
Useful as a gaurd at the start of a sequence, that is waiting for an event to trigger after the sequence has started (i.e. been initialised).
Wating for the Next Thing, Starting from the Last
clearing_policy ==
ON_SUCCESS
Useful as a guard watching for an event that could have come in anytime, but for which we do with to reset (and subsequently look for the next event). e.g. button events.
- Parameters
topic_name (str) – name of the topic to connect to
topic_type (Any) – class of the message type (e.g.
std_msgs.msg.String)qos_profile (rclpy.qos.QoSProfile) – qos profile for the subscriber
name (str) – name of the behaviour
clearing_policy – when to clear the data
py_trees_ros.transforms
Various behaviours that enable common interactions with ROS transforms.
- class py_trees_ros.transforms.FromBlackboard(name, variable_name, target_frame, source_frame, static, qos_profile, static_qos_profile=None)[source]
Bases:
BehaviourBroadcast a transform from the blackboard using the transform broadcaster mechanisms.
If no it fails to find a geometry_msgs.Transform object on the blackboard, or the blackboard variable is None, this behaviour will update with status
FAILURE.- Parameters
variable_name (str) – name of the transform variable on the blackboard
target_frame (str) – name of the frame to transform into
source_frame (str) – name of the input frame
static (bool) – designate whether it is a static transform or otherwise
qos_profile (rclpy.qos.QoSProfile) – qos profile for the non-static broadcaster
static_qos_profile (rclpy.qos.QoSProfile) – qos profile for the static broadcaster (default: use tf2_ros’ defaults)
name (str) – name of the behaviour
- class py_trees_ros.transforms.ToBlackboard(name, variable_name, target_frame, source_frame, qos_profile, static_qos_profile=None, clearing_policy=ClearingPolicy.ON_INITIALISE)[source]
Bases:
BehaviourBlocking behaviour that looks for a transform and writes it to a variable on the blackboard.
If it fails to find a transform immediately, it will update with status
RUNNINGand write ‘None’ to the blackboard.Tip
To ensure consistent decision making, use this behaviour up-front in your tree’s tick to record a transform that can be locked in for the remainder of the tree tick.
Usage Patterns
clearing_policy ==
ON_INTIALISE
Use if you have subsequent behaviours that need to make decisions on whether the transform was received or not.
clearing_policy ==
NEVER
Never clear the result. Useful for static transforms or if you are doing your own lookup on the timestamps for any relevant decision making.
- Parameters
variable_name – name of the key to write to on the blackboard
target_frame (str) – name of the frame to transform into
source_frame (str) – name of the input frame
qos_profile (rclpy.qos.QoSProfile) – qos profile for the non-static subscriber
static_qos_profile (rclpy.qos.QoSProfile) – qos profile for the static subscriber (default: use tf2_ros’ defaults)
name (str) – name of the behaviour
clearing_policy (ClearingPolicy) –
- Raises
TypeError – if the clearing policy is neither
ON_INITIALISEorNEVER
- initialise()[source]
Clear the blackboard variable (set to ‘None’) if using the
ON_INTIALISEpolicy.
py_trees_ros.trees
The py_trees_ros.trees.BehaviourTree class
extends the core py_trees.trees.BehaviourTree class
with both blackboard and (tree) snapshot streaming services.
Interact with these services via the py-trees-blackboard-watcher and
py-trees-tree-watcher command line utilities.
- class py_trees_ros.trees.BehaviourTree(root, unicode_tree_debug=False)[source]
Bases:
BehaviourTreeExtend the
py_trees.trees.BehaviourTreeclass with a few bells and whistles for ROS.- ROS Parameters:
default_snapshot_stream: enable/disable the default snapshots stream in ~/snapshots` (default: False)
default_snapshot_period: periodically publish (default:
math.inf)default_snapshot_blackboard_data: include tracking and visited variables (default: True)
default_snapshot_blackboard_activity: include the blackboard activity (default: False)
setup_timeout: time (s) to wait (default:
math.inf)if
math.inf, it will block indefinitely
- ROS Publishers:
~/snapshots (
py_trees_interfaces.msg.BehaviourTree): the default snapshot stream, if enabled
- ROS Services:
~/blackboard_streams/close (
py_trees_ros_interfaces.srv.CloselackboardWatcher)~/blackboard_streams/get_variables (
py_trees_ros_interfaces.srv.GetBlackboardVariables)~/blackboard_streams/open (
py_trees_ros_interfaces.srv.OpenBlackboardWatcher)~/snapshot_streams/close (
py_trees_ros_interfaces.srv.CloseSnapshotsStream)~/snapshot_streams/open (
py_trees_ros_interfaces.srv.OpenSnapshotsStream)~/snapshot_streams/reconfigure (
py_trees_ros_interfaces.srv.ReconfigureSnapshotsStream)
Topics and services are not intended for direct use, but facilitate the operation of the utilities py-trees-tree-watcher and py-trees-blackboard-watcher.
- Parameters
- Raises
AssertionError – if incoming root variable is not the correct type
- setup(node=None, node_name='tree', timeout=Duration.INFINITE, visitor=None, **kwargs)[source]
Setup the publishers, exchange and add ROS relevant pre/post tick handlers to the tree. Ultimately relays this call down to all the behaviours in the tree.
- Parameters
node (Optional[rclpy.node.Node]) – Optional ROS Node object. If None (default), creates its own node.
node_name (str) – Name of ROS node created. Only takes effect if node is None.
timeout (float) – time (s) to wait (use common.Duration.INFINITE to block indefinitely)
visitor (Optional[VisitorBase]) – runnable entities on each node after it’s setup
**kwargs (int) – distribute args to this behaviour and in turn, to it’s children
- Raises
- Parameters
node (Optional[rclpy.node.Node]) –
node_name (str) –
timeout (float) –
visitor (Optional[VisitorBase]) –
kwargs (int) –
- tick_tock(period_ms, number_of_iterations=-1, pre_tick_handler=None, post_tick_handler=None)[source]
Tick continuously at the period specified.
This is a re-implementation of the
tick_tock()tick_tock that takes advantage of the rclpy timers so callbacks are interleaved inbetween rclpy callbacks (keeps everything synchronous so no need for locks).
- class py_trees_ros.trees.SnapshotStream(node, topic_name=None, parameters=None)[source]
Bases:
objectSnapshotStream instances are responsible for creating / destroying a snapshot stream as well as the configurable curation of snapshots that are published on it.
- Parameters
node (rclpy.node.Node) –
topic_name (str) –
parameters (SnapshotStream.Parameters) –
- class Parameters(blackboard_data=False, blackboard_activity=False, snapshot_period=Duration.INFINITE)[source]
Bases:
objectReconfigurable parameters for the snapshot stream.
- static expand_topic_name(node, topic_name)[source]
Custom name expansion depending on the topic name provided. This is part of the stream configuration on request which either provides no hint (automatic name generation), a simple hint (relative name expanded under the snapshot streams namespace) or a complete hint (absolute name that does not need expansion).
- Parameters
node (rclpy.node.Node) – node used to reference the absolute namespace if the hint is not absolute
topic_name (str) – hint for the topic name
- Returns
the expanded topic name
- Return type
- publish(root, changed, statistics, visited_behaviour_ids, visited_blackboard_client_ids)[source]
” Publish a snapshot, including only what has been parameterised.
- Parameters
root (Behaviour) – the tree
changed (bool) – whether the tree status / graph changed or not
statistics (<Mock name='mock.msg.Statistics' id='140605245586304'>) – add tree statistics to the snapshot data
visited_behaviour_ids (Set[UUID]) – behaviours on the visited path
visited_blackboard_client_ids (Set[UUID]) – blackboard clients belonging to behaviours on the visited path
- class py_trees_ros.trees.Watcher(topic_name=None, namespace_hint=None, parameters=None, statistics=False, mode=WatcherMode.SNAPSHOTS)[source]
Bases:
objectThe tree watcher sits on the other side of a running
BehaviourTreeand is a useful mechanism for quick introspection of it’s current state.- Parameters
topic_name (str) – location of the snapshot stream (optional)
namespace_hint (str) – refine search for snapshot stream services if there is more than one tree (optional)
parameters (Parameters) – snapshot stream configuration controlling both on-the-fly stream creation and display
statistics (bool) – display statistics
mode (WatcherMode) –
See also
- callback_snapshot(msg)[source]
Formats the string message coming in.
- Args
msg (
py_trees_ros_interfaces.msg.BehaviourTree):serialised snapshot
- create_service_client(key)[source]
Convenience api for opening a service client and waiting for the service to appear.
- Parameters
key (str) – one of ‘open’, ‘close’.
- Raises
NotReadyError – if setup() wasn’t called to identify the relevant services to connect to.
TimedOutError – if it times out waiting for the server
- setup(timeout_sec)[source]
Creates the node and checks that all of the server-side services are available for calling on to open a connection.
- Parameters
timeout_sec (float) – time (s) to wait (use common.Duration.INFINITE to block indefinitely)
- Raises
NotFoundError – if services/topics were not found
MultipleFoundError – if multiple services were found
TimedOutError – if service clients time out waiting for the server
- class py_trees_ros.trees.WatcherMode(value)[source]
Bases:
EnumAn enumerator specifying the view mode for the watcher
- DOT_GRAPH = 'DOT_GRAPH'
Render with the dot graph representation of the static tree (using an application or text to console).
- SNAPSHOTS = 'SNAPSHOTS'
Render ascii/unicode snapshots from a snapshot stream
py_trees_ros.utilities
Assorted utility functions.
- class py_trees_ros.utilities.Publishers(node, publisher_details, introspection_topic_name='publishers')[source]
Bases:
objectUtility class that groups the publishers together in one convenient structure.
- Parameters
(obj (publisher_details) – tuple): list of (str, str, msgType, bool, int) tuples representing (unique_name, topic_name, publisher_type, latched) specifications for creating publishers
Examples
Convert the incoming list of specifications into proper variables of this class.
publishers = py_trees.utilities.Publishers( [ ('foo', '~/foo', std_msgs.String, True, 5), ('bar', '/foo/bar', std_msgs.String, False, 5), ('foobar', '/foo/bar', std_msgs.String, False, 5), ] )
- class py_trees_ros.utilities.Services(node, service_details, introspection_topic_name='services')[source]
Bases:
objectUtility class that groups services together in one convenient structure.
- Parameters
(obj (service_details) – tuple): list of (str, str, srvType, func) tuples representing (unique_name, topic_name, service_type, callback) specifications for creating services
Examples
Convert the incoming list of specifications into proper variables of this class.
services = py_trees.utilities.Services( [ ('open_foo', '~/get_foo', foo_interfaces.srv.OpenFoo, open_foo_callback), ('open_foo', '/foo/open', foo_interfaces.srv.OpenFoo, self.open_foo_callback), ('get_foo_bar', '/foo/bar', foo_interfaces.srv.GetBar, self.foo.get_bar_callback), ] )
- class py_trees_ros.utilities.Subscribers(node, subscriber_details, introspection_topic_name='subscribers')[source]
Bases:
objectUtility class that groups subscribers together in one convenient structure.
- Parameters
(obj (subscriber_details) – tuple): list of (str, str, msgType, bool, func) tuples representing (unique_name, topic_name, subscriber_type, latched, callback) specifications for creating subscribers
Examples
Convert the incoming list of specifications into proper variables of this class.
subscribers = py_trees.utilities.Subscribers( [ ('foo', '~/foo', std_msgs.String, True, foo), ('bar', '/foo/bar', std_msgs.String, False, self.foo), ('foobar', '/foo/bar', std_msgs.String, False, foo.bar), ] )
- py_trees_ros.utilities.basename(name)[source]
Generate the basename from a ros name.
- Parameters
name (
str) – ros name- Returns
name stripped up until the last slash or tilde character.
- Return type
Examples
basename("~dude") # 'dude' basename("/gang/dude") # 'dude'
- py_trees_ros.utilities.create_anonymous_node_name(node_name='node')[source]
Creates an anonoymous node name by adding a suffix created from a monotonic timestamp, sans the decimal.
- Returns
the unique, anonymous node name
- Return type
- py_trees_ros.utilities.find_service(node, service_type, namespace=None, timeout=0.5)[source]
Discover a service of the specified type and if necessary, under the specified namespace.
- Parameters
node (
rclpy.node.Node) – nodes have the discovery methodsservice_type (
str) – primary lookup hintnamespace (
str) – secondary lookup hinttimeout (float) – immediately post node creation, can take time to discover the graph (sec)
- Returns
fully expanded service name
- Return type
- Raises
NotFoundError – if no services were found
MultipleFoundError – if multiple services were found
- py_trees_ros.utilities.find_topics(node, topic_type, namespace=None, timeout=0.5)[source]
Discover a topic of the specified type and if necessary, under the specified namespace.
- Parameters
node (rclpy.node.Node) – nodes have the discovery methods
topic_type (str) – primary lookup hint
timeout (float) – check every 0.1s until this timeout is reached (can be None -> checks once)
- Return type
- py_trees_ros.utilities.get_py_trees_home()[source]
Find the default home directory used for logging, bagging and other esoterica.
- py_trees_ros.utilities.qos_profile_latched()[source]
Convenience retrieval for a latched topic (publisher / subscriber)
- py_trees_ros.utilities.qos_profile_unlatched()[source]
Default profile for an unlatched topic (in py_trees_ros).
- py_trees_ros.utilities.resolve_name(node, name)[source]
Convenience function for getting the resolved name (similar to ‘publisher.resolved_name’ in ROS1).
- Parameters
node (
rclpy.node.Node) – the node, namespace it should be relevant to(obj (name) – str): topic or service name
Note
This entirely depends on the user providing the relevant node, name pair.
py_trees_ros.visitors
ROS Visitors are entities that can be passed to a ROS tree implementation
(e.g. BehaviourTree) and used to either visit
each and every behaviour in the tree, or visit behaviours as the tree is
traversed in an executing tick. At each behaviour, the visitor
runs its own method on the behaviour to do as it wishes - logging, introspecting).
Warning
Visitors should not modify the behaviours they visit.
See also
The base interface and core visitors in py_trees.visitors
- class py_trees_ros.visitors.SetupLogger(node)[source]
Bases:
VisitorBaseUse as a visitor to
py_trees_ros.trees.TreeManager.setup()to log the name and timings of each behaviours’ setup to the ROS debug channel.- Parameters
node (rclpy.node.Node) – an rclpy node that will provide debug logger
- class py_trees_ros.visitors.TreeToMsgVisitor[source]
Bases:
VisitorBaseVisits the entire tree and gathers all behaviours as messages for the tree logging publishers.
- Variables
tree (
py_trees_msgs.msg.BehaviourTree) – tree representation in message form
py_trees_ros.programs
Entry points to the programs (tools and utilities).
py_trees_ros.programs.blackboard_watcher
Open up a window onto the blackboard!
Introspect on the entire blackboard or a part thereof and receive a stream of updates whenever values change.
Examples:
# list all keys on the blackboard
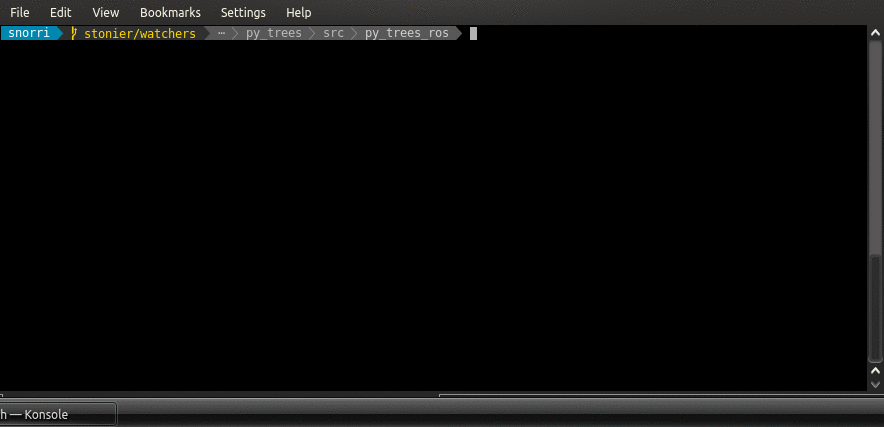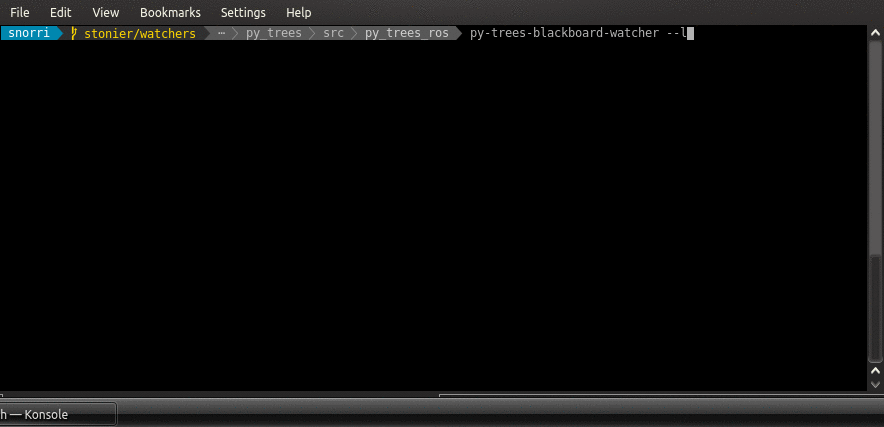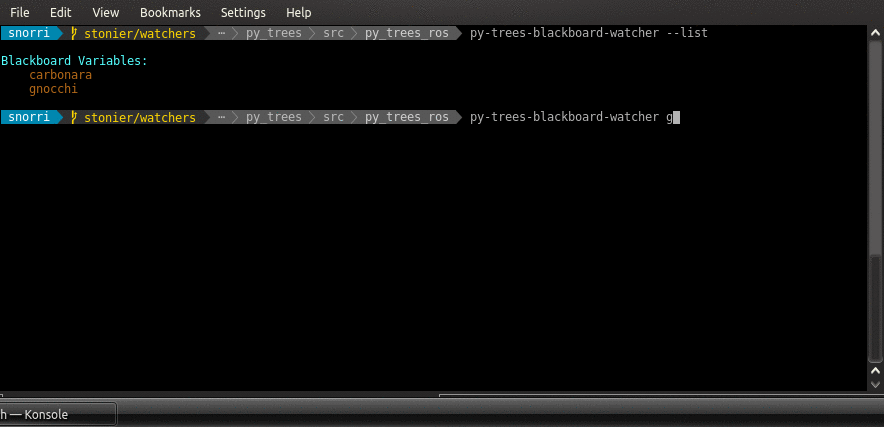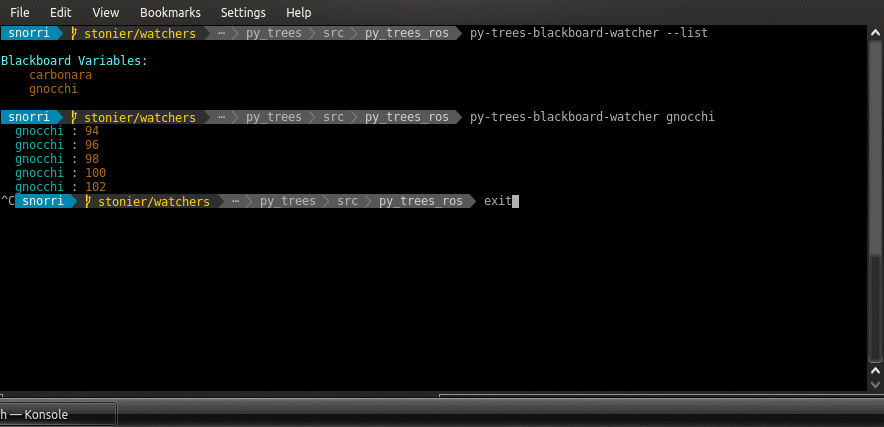
$ py-trees-blackboard-watcher --list
# stream all variables
$ py-trees-blackboard-watcher
# stream only visited variables and access details
$ py-trees-blackboard-watcher --visited --activity
# stream a single variable
$ py-trees-blackboard-watcher odometry
# stream only a single field within a variable
$ py-trees-blackboard-watcher odometry.pose.pose.position
usage: py-trees-blackboard-watcher [-h] [-l] [-a] [-v] [-n [NAMESPACE]] ...
Positional Arguments
- variables
space separated list of blackboard variable names (may be nested) to watch
Default: []
Named Arguments
- -l, --list
list the blackboard variable names
- -a, --activity
include the logged activity stream for recent changes
Default: False
- -v, --visited
filter selected keys from those associated with behaviours on the most recent tick’s visited path
Default: False
- -n, --namespace
namespace of blackboard services (if there should be more than one blackboard)
Example interaction with the services of an py_trees_ros.blackboard.Exchange:
- py_trees_ros.programs.blackboard_watcher.main(command_line_args=['-T', '-E', '-W', '--keep-going', '-b', 'html', '-d', '_build/doctrees', '-D', 'language=en', '.', '/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/py-trees-ros/checkouts/devel/_readthedocs//html'])[source]
Entry point for the blackboard watcher script.
py_trees_ros.programs.tree_watcher
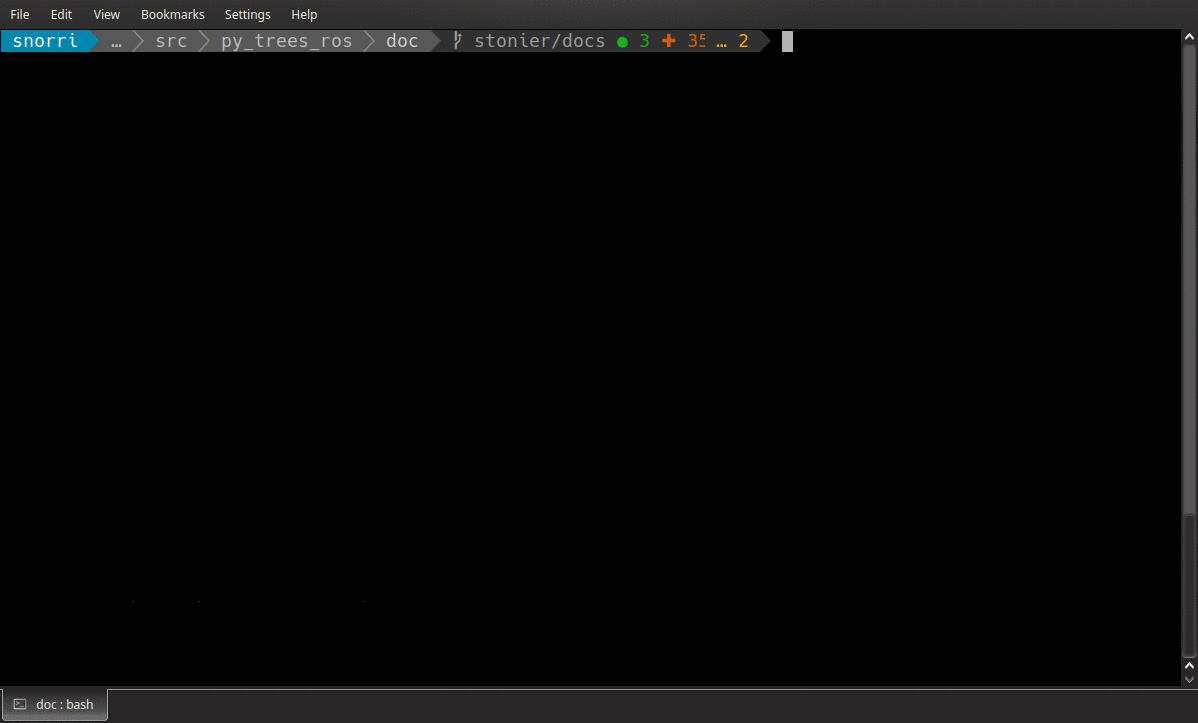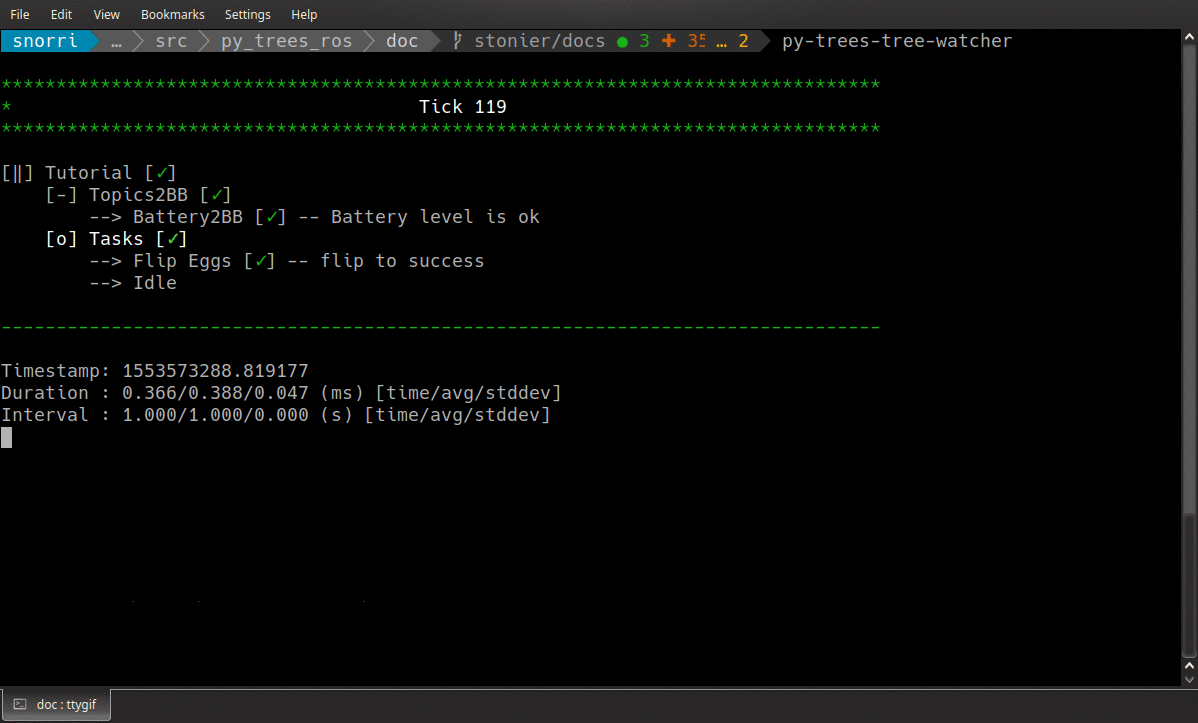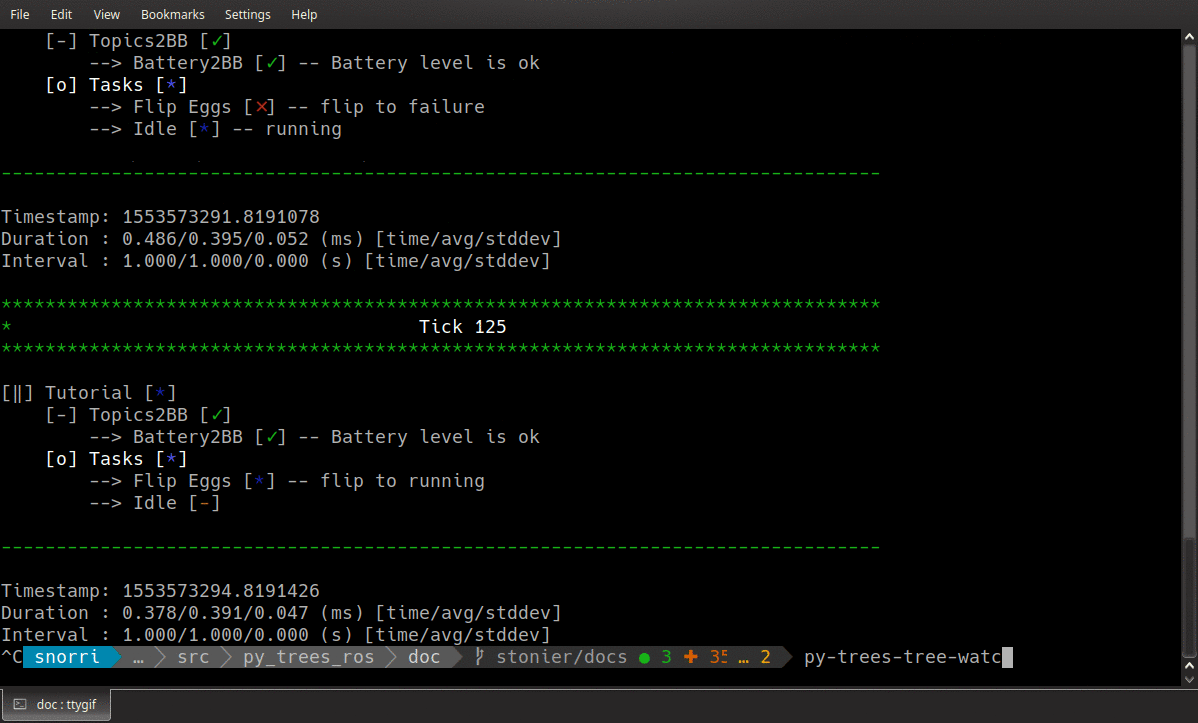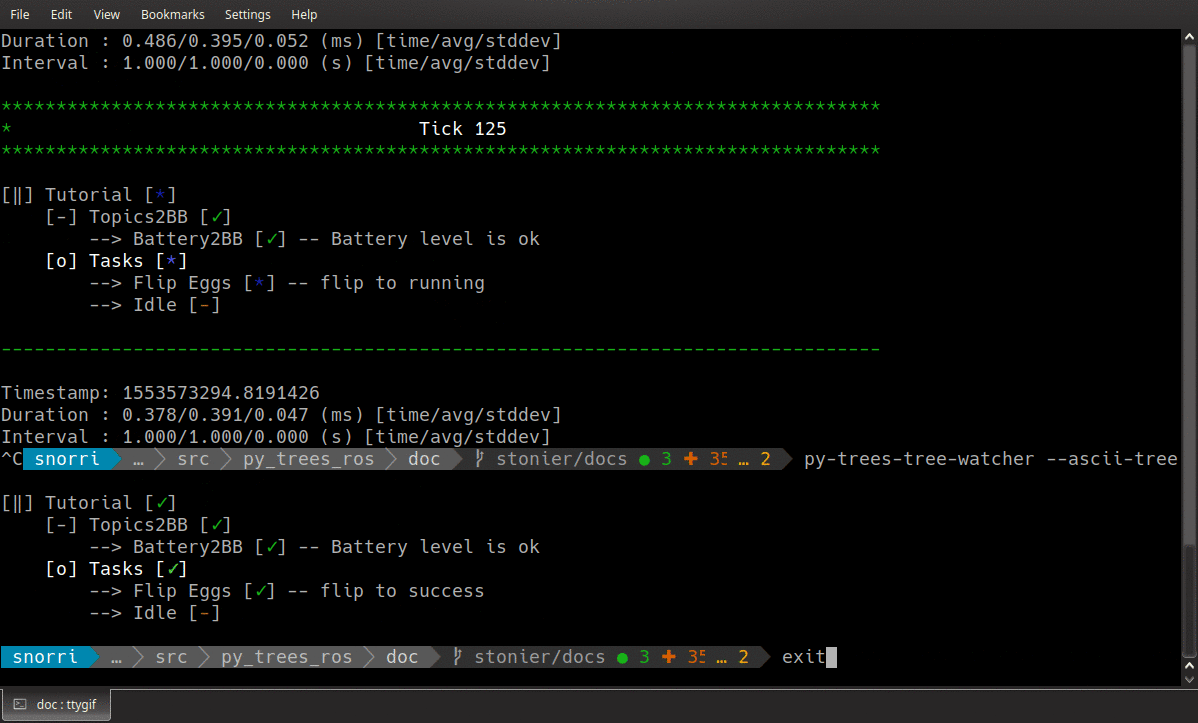
Open up a window onto the behaviour tree!
Render a oneshot snapshot of the tree as a dot graph, or stream it and it’s state continuously as unicode art on your console. This utility automatically discovers the running tree and opens interfaces to that, but if there is more than one tree executing use the namespace argument to differentiate between trees.
Examples:
# render the tree as a dot graph (does not include runtime information)
$ py-trees-tree-watcher --dot-graph
# connect to an existing snapshot stream (e.g. the default, if it is enabled)
$ py-trees-tree-watcher /tree/snapshots
# open and connect to a snapshot stream, visualise the tree graph and it's changes only
$ py-trees-tree-watcher
# open a snapshot stream and include visited blackboard variables
$ py-trees-tree-watcher -b
# open a snapshot stream and include blackboard access details (activity)
$ py-trees-tree-watcher -a
# open a snapshot stream and include timing statistics
$ py-trees-tree-watcher -s
usage: py-trees-tree-watcher [-h] [-n [NAMESPACE_HINT]] [-a] [-b] [-s]
[--snapshots | --dot-graph]
[topic_name]
Positional Arguments
- topic_name
snapshot stream to connect to, will create a temporary stream if none specified
Named Arguments
- -n, --namespace-hint
namespace hint snapshot stream services (if there should be more than one tree)
- -a, --blackboard-activity
show logged activity stream (streaming mode only)
Default: False
- -b, --blackboard-data
show visited path variables (streaming mode only)
Default: False
- -s, --statistics
show tick timing statistics (streaming mode only)
Default: False
- --snapshots
render ascii/unicode snapshots from a snapshot stream
- --dot-graph
render the tree as a dot graph
Command line utility that introspects on a running
BehaviourTree instance over it’s snapshot
stream interfaces. Use to visualise the tree as a dot graph or
track tree changes, timing statistics and blackboard variables visited
by the tree on each tick.